Corynebacterium Kutscheri Causes Which of the Following in Rats
Pathology of Corynebacterium kutscheri in rats. The organism is carried in the upper respiratory system and is transmitted by direct contact between mother and babies by sexual transfer through the air over short.

2018 Rat Gross Path Flashcards Quizlet
Dole et al 2013.
. Kutscheri causes latent infection in healthy mice and rats but can cause severe illness when an animal is immunocompromised or nutritionally deficient 1 3a 9 10. Estrous cycle length in female mice is 45 days and estrus. Corynebacterium kutscheri Coronavirus.
Corynebacterium kutscheri a gram positive and acid- alcohol resistant slightly curved bacillus causes an infection in rodents called murine corynebacteriosis which was named at. Corynebacterium bovis has been associated with hyperkeratosis especially in immunodeficient mice Clifford et al 1995. Active disease is precipitated by immunosuppression or.
Kutscheri infection is often subclinical in otherwise healthy mice. Kutscheri causes latent infection in healthy mice and rats but can cause severe illness when an animal is immunocompromised or nu-. If barbering is a concern within a colony the animal _________ hair loss should be removed from the enclosure.
Sex differences in susceptibility of ICR mice to oral infection with Corynebacterium kutscheri. Streptococcus pneumoniae and Corynebacterium kutscheri are potent respiratory pathogens in the rat but seldom in the absence of some combination involving M. TABLE 9 Agents Grouped According to Importance as Causes of Natural Respiratory Disease.
Corynebacterium kutscheri infection of skin and soft tissue following rat bite. Corynebacterium kutscheri is a gram-positive coryneform club-shaped bacterium which can be found in soil sewage and marine environments and has been explored for possible utility of bioremediation of oil spills Oyetibo et al 2013. Common in conventional rats enveloped ss RNA virus Formerly called SDAV or SDAVRCV Many strains with varying predilection for salivary gland most common to upper respiratory tract to lower respiratory tract Rat Coronavirus SDAVRCV common to upper respiratory tract to lower respiratory tract.
Where anaerobic or mycobacterial infection is suspected then the labora-tory should be made aware of this. In rats mice guinea pigs and hamsters C. Komukai Y Amao H Goto N Kusajima Y Sawada T Saito M Takahashi KW.
For example Corynebacterium kutscheri is for the most part a commensal bacterium in mice rats and voles causing a latent infection in some healthy mice and rats. Diagnosis and therapy Diagnosis should be made on the basis of clinical signs cytology of lesions and culture. Rats and mice are primarily nocturnal creatures.
Corynebacterium kutscheri can cause furunculosis and cutaneous pyogranulomas and occasionally necrosis and sloughing of the extremities. Corynebacteria cause infections in animals and in rare cases animals serve as the source of corynebacteria that subsequently cause disease in humans. 20 was first described in 1894 by KUTSCHFR.
Respiratory disease in rats is caused primarily by infectious agents such as Mycoplasma pulmonis Streptococcus pneumoniae Corynebacterium kutscheri cilia associated respiratory CAR bacillus Sendai virus and coronavirus. Which species has two pairs incisors with a smaller pair peg teeth found behind the large pair. Mycoplasma pulmonis the organism that almost all rats in the general pet population carry is the cause of the majority of respiratory and genital infections in rats.
Inamorechronicbacterial infection dueto Corynebacterium kutscheri. Kutscheri is a gram positive rod that causes caseous purulent foci in the lungs of rats when stressed. Pulmonis Sendai virus andor CAR bacillus.
It is often reported as chronic respiratory syndrome of multifactorial aetiology where two or more agents are involved. Kutscheri is the cause of pseudotuberculosis although in. The infection is usually subclinical.
- Acetylcholine induced the contraction of myoepithelial cells squeezing out the contents of the secretory cells of. Is part of the normal flora found in the GI tract of rats and mice. Immunological processes following microbial invasion are generally recognized as important.
Indomethacin fed con-tinuously to rats for 80 days at maximal tolerated levels caused no. Weaning takes place at 21 days. Corynebacterium kutscheri a gram-positive diphtheroid bacillus causes a relatively common spontaneous disease of rats and mice Carlton and Hunt 1978.
The maximal tolerated level caused no observable adverse effects on host resistance. Gross solitary or multiple abscesses due to septic emboli lung liver kidney skin and joints - lung most frequently affected in the rat. J Clin Microbiol 453468-3469.
When rats are stressed they may produce more porphyrin from their Harderian glands. Illness is characterized by bacteremia with septic emboli and end-organ disease in the kidneys and livers of mice and the lungs of rats 3a 9 10. Corynebacterium kutscheri is a common bacterium isolated from the oral cavity of healthy mice and rats.
Clinical signs include dyspnea oculonasal discharge rough hair coat and hunched posture. Corynebacterium kutscheri is the cause of pseudotuberculosis in mice and rats. Study done in 1940 by Tashiro et al.
Also known as pseudotuberculosis3 5 139 15 21 and Corynebacterium psetdotzbercuiossir7. Medical Corner - Mycoplasmosis in the Pet Rat. Indeed a single Corynebacterium kutscheri infection induced the upregulation of Gal-3 in the lungs of rats Won et al 2007 while the synthesis and.
Percy DH Barthold SW. Pneumonia in Rats Due to Infection with Corynebacterium kutscheri WE. We report the first well-documented case of C.
Rats have an average litter size of 818 pups. Both male and female mice are sexually mature by 68 weeks and have a breeding life of 9 months. The microorganism was identified by conventional biochemical tests and confirmed by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis.
Scanziani et al 1998. WHITEHAIR The disease produced by infection with Corynebacterium kwtscberi. When an animal is immunocompromised nutritionally.
Kutscheri human infection which followed a rat bite. This disease was first reported in mice by Kutscher 1894 in Germany and by Welch Reed 1902 in the United States whereas Reed conducted the first experimental studies with the organism. Histo Caseous necrosis surrounded by epithelioid macrophages and multinucleated giant cells.
To demonstrate that an injection of acetylcholine in the rat induced quick excretion of bloody tears.

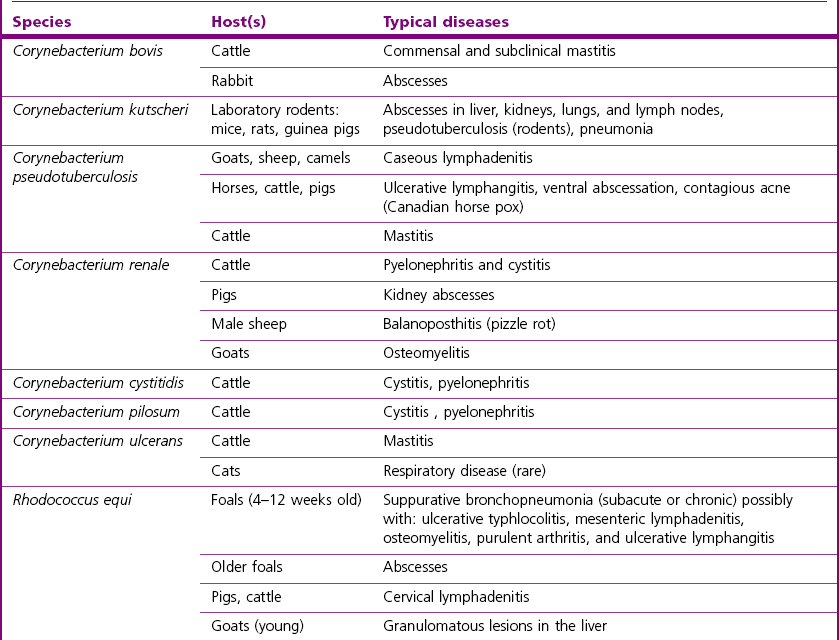
Corynebacterium Species And Rhodococcus Equi Veterian Key


No comments for "Corynebacterium Kutscheri Causes Which of the Following in Rats"
Post a Comment